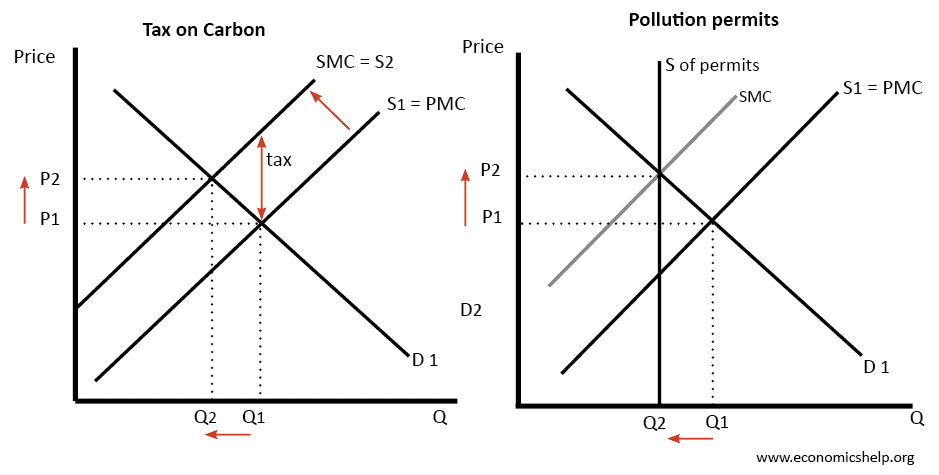
carbon tax vs cap and trade pros and cons
It provides more certainty about the amount of emissions reductions that will result and little certainty about the price of emissions which is set by the emissions trading market. Cap-and-trade sets the quantity of emissions reductions and lets the.
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
Entities that have an overall increase in sequestered carbon may be eligible to sell the extra as carbon credit trade.

. Both the carbon tax and the ETS reduce emissions by putting a cost on carbon emissions. It is a form of carbon pricing and aims to reduce global carbon emissions in order to mitigate the global warming issue. Although the carbon tax has some important advantages it also implies some problems.
Yale Environment 360 Editor Roger Cohn asked eight climate policy experts all favoring controls but differing on cap-and-trade versus taxes to spell out their positions. The pros and cons of both approaches are neatly summarized in a May 7 posting at the Yale Environment 360 website. A carbon tax or a cap-and-trade system.
Several analyses have claimed that a carbon tax is superior to cap and trade in terms of the ability to achieve a fair distribution of the policy burden between polluters firms and consumers to preserve international competitiveness or to avoid problems associated with. This can be implemented either through a carbon tax known as a price instrument or a cap-and-trade scheme a so-called quantity instrument. November 2019 Paper There is widespread agreement among economists and a diverse set of other policy analysts that at least in the long run an economy-wide carbon-pricing system will be an essential element of any national policy that can achieve meaningful reductions of CO2 emissions costeffectively in the United States and many other countries.
Economists love discussing the pros and cons of a carbon tax versus the cap-and-trade system. It could start a race for lower emissions technologies which would give energy companies an edge on competitors. A government entity sets a limit cap on the amount of a pollutant such as carbon dioxide or another greenhouse gas.
Stavins1 Harvard Kennedy School This paper compares the two major approaches to carbon pricing carbon taxes and cap and trade in the context of a possible future climate policy and does so. Cap and trade. Swift and deep reductions in emissions of greenhouse gases chiefly carbon dioxide are necessary to help avoid some of the most devastating effects of climate change.
One aspect of US climate policy that is particularly contentious is the issue of the best economic tool to employ to reduce emissions. Simply put the less fossil fuel used the less the tax affects the company. No matter how much gets emitted a carbon tax makes the emission the same.
Theory and practice Robert N. Although no option dominates the others a key finding is that exogenous emissions pricing whether through a carbon tax or through the hybrid option has a number of important attractions over pure cap and trade. A carbon tax imposes a tax on each unit of greenhouse gas emissions and gives firms and households depending on the scope an incentive to reduce pollution whenever doing so would cost less than.
I believe carbon taxes are the better of the two options because it is simple and immediately causes companies and individuals of ways to reduce fuel and energy consumption. Although cap-and-trade is the most cost-efficient option for firms more revenue from a carbon tax system can be used by the government to fund spending or reduce other taxes. I believe both systems have their merits and utilizing either one would positively affect climate change and the economy.
A carbon tax has a major advantage over cap-and-trade and a hybrid version because it allows for carbon price certainty is less costly to administer and is a substantial source of revenue. Those in favor of cap and trade argue that it is the only approach that can guarantee that an environmental objective will be achieved has been shown to effectively work to protect the environment at lower than expected costs and is politically more attractive. Each approach has its vocal supporters.
I believe carbon taxes are the better of the two options because it is simple and immediately causes companies and individuals of ways to reduce fuel and energy consumption. However they do it in slightly different ways. Carbon sequestration commonly occurs in agriculture via an increase in.
Cap-and-trade has one key environmental advantage over a carbon tax. The downside is that you need to guess how high to. With a carbon tax there is an immediate cost to firms for polluting.
Comparison of Carbon Tax and Cap Trade. Comparison of Carbon Tax and Cap. The carbon tax can be regarded as the price for one unit of carbon that is emitted into our atmosphere.
Essentially a carbon tax sets a fixed price for carbon emissions while the ETS sets a fixed quantity of emissions. Those supporting a carbon tax argue that it is a better approach because it is. Carbon taxes and cap-and-trade schemes are two ways to put a price on carbon pollution each with its own pros and cons Skip to.
However a cap-and-trade policy offers its own advantages in that emissions allowances can be allocated so as to minimize the policys negative effects on competitiveness and prevent. Plus some conservatives may be attracted to a carbon tax as an alternative to more EPA regulations. Carbon taxes vs.
Now that weve explored both the option of implementing a carbon tax for emissions or regulating them under a cap and trade scheme lets take a closer look at what the differences are. Emissions trading or cap-and-trade CAT and a carbon tax are fundamentally different tools to limit the effects of using fossil fuels. A carbon tax sets the price of carbon dioxide emissions and allows the market to determine the quantity of emission reductions.
This can be implemented either through a carbon tax known as a. Taken where we have discussed cap trade vs. A carbon tax is a simpler blunter tool which is easier to administer and regulate.
Both measures are attempts to reduce environmental damage without causing undue economic hardship to the industry. Beyond helping prevent price volatility and reducing expected policy errors in the face of uncertainties exogenous pricing helps avoid. A carbon tax could force businesses and citizens to cut back carbon-intensive services and goods.
Carbon taxes makes emitting carbon dioxide more expensive. Proponents of cap and trade argue that it is a palatable alternative to a carbon tax.

The Pros And Cons Of Carbon Taxes And Cap And Trade Systems Semantic Scholar
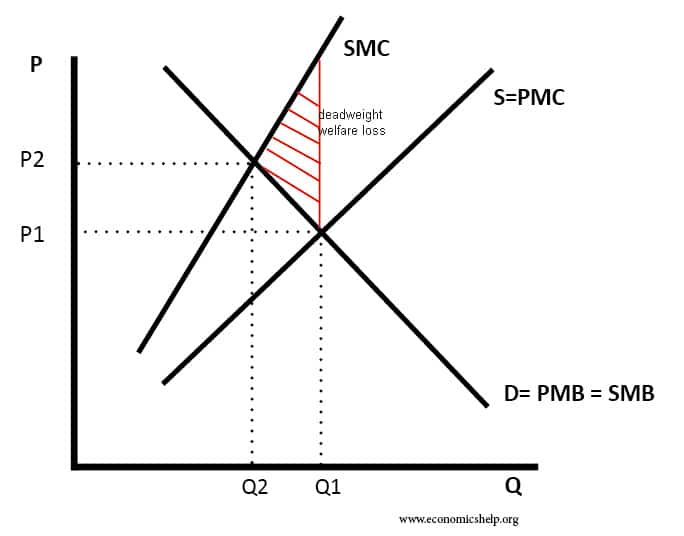
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help

Seneca Esg Pricing Carbon Emissions Trading Schemes Part 1

The Pros And Cons Of Carbon Taxes And Cap And Trade Systems Semantic Scholar
Difference Between Carbon Tax And Emissions Trading Scheme Difference Between

World Regional Geography Unit I Introduction To World Regional Geography Lesson 4 Solutions To Global Warming Debate Ppt Download

Economics And Policy At The 49th Parallel Economists Are Like Accountants Except Without The Personality

Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
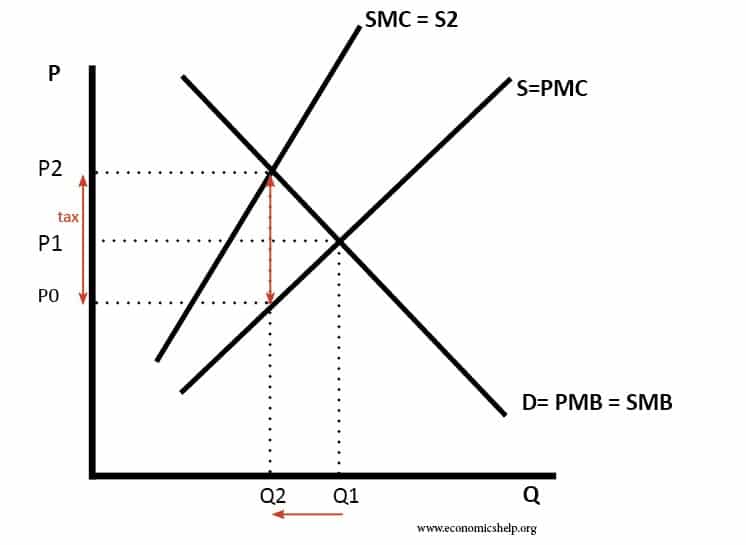
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help
Difference Between Carbon Tax And Emissions Trading Scheme Difference Between
Difference Between Carbon Tax And Emissions Trading Scheme Difference Between

Carbon Taxes And Cap And Trade State Policy Options Muninet Guide

27 Main Pros Cons Of Carbon Taxes E C
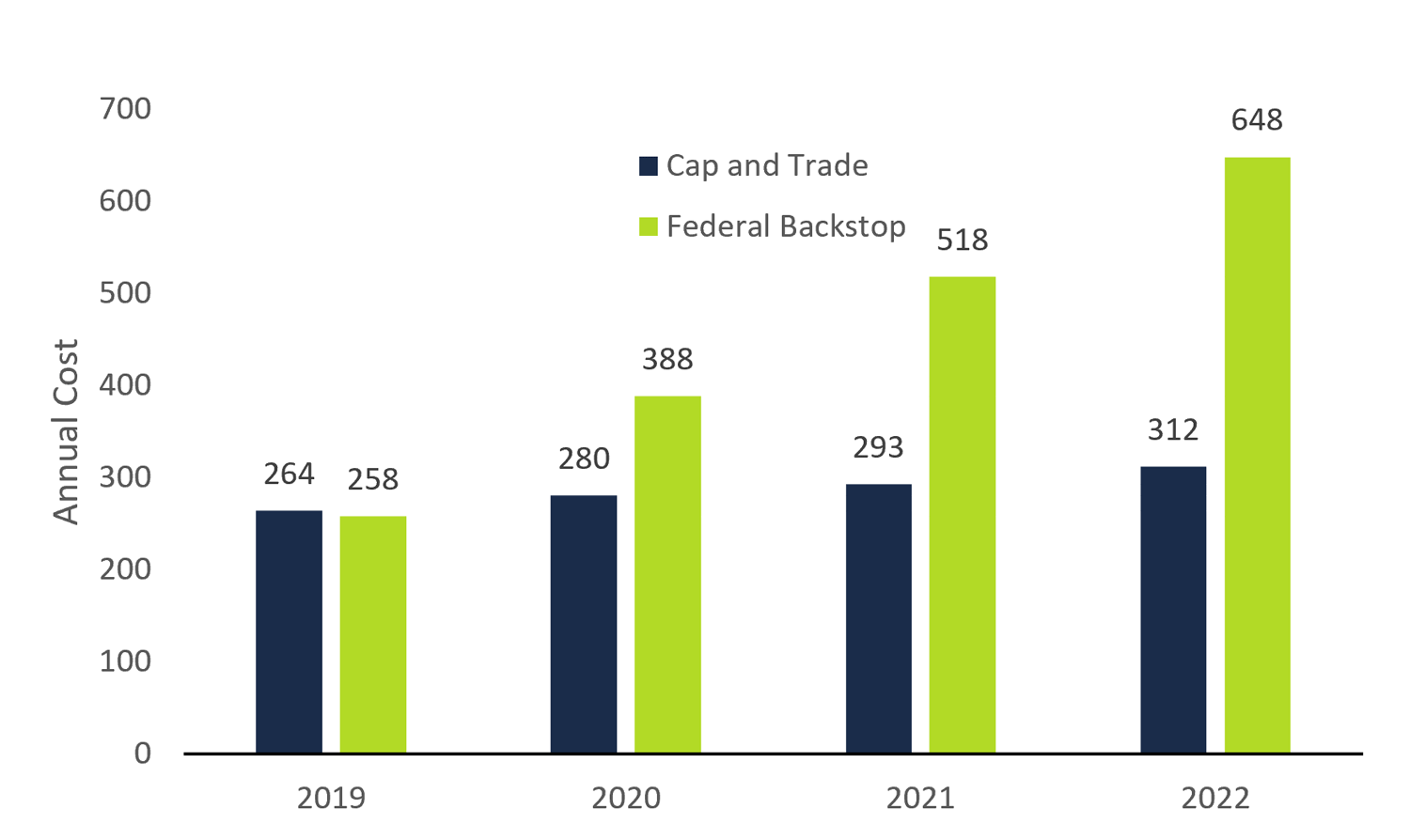
Cap And Trade A Financial Review Of The Decision To Cancel The Cap And Trade Program
Carbon Tax Vs Cap And Trade Which Is Better R Economics
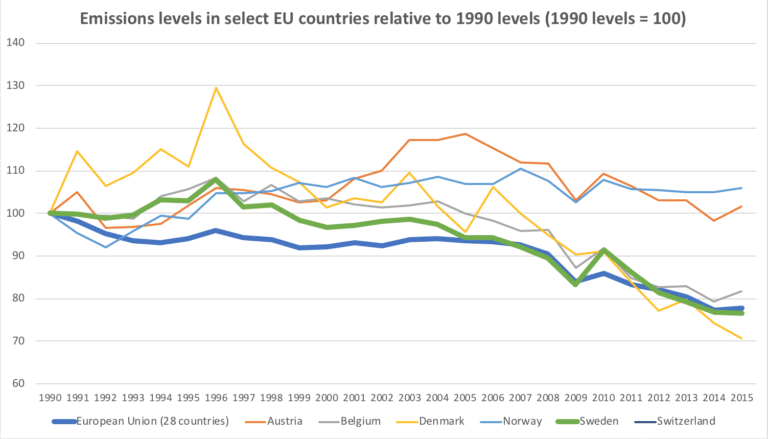
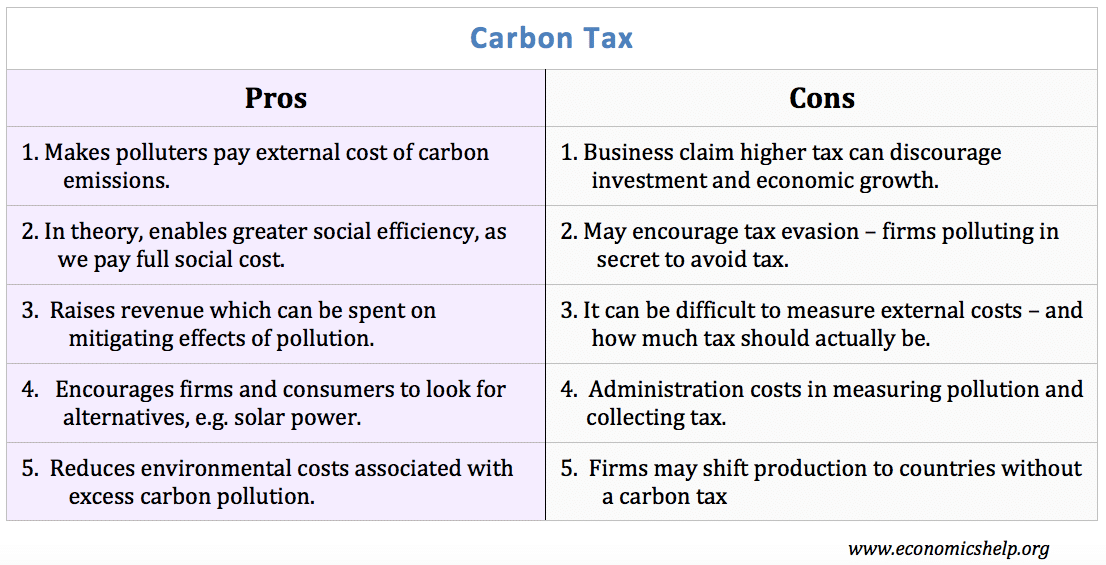
Carbon Tax Pros And Cons Economics Help